Which Type of Viruses Can Be Directly Used for Translation
The viral RNA is translated directly into new viral proteins after infection by the virus. Translation as related to genomics is the process through which information encoded in messenger RNA mRNA directs the addition of amino acids during protein synthesis.

22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts
The RNA virus group can be subdivided based on the type of RNA that serves as the genome.
. Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Aneuploidy chromosomal rearrangements. The following resource was originally accessed through the BioSciEd Net BEN digital resources collection which is the National Science Digital Library NSDL Pathway for biological sciences education.
The viral capsid is removed and degraded by viral enzymes or host enzymes releasing the viral genomic nucleic acid. DNA viruses that use reverse trThe hepadnaviruses contain a DNA. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies the virus continues infecting new hosts.
If a virus has a ssRNA genome it can be translated directly to make viral proteins. Positive ssRNA If the hypothesis stating viruses evolved prior to living organisms on Earth is true the first type of viruses in the world were likely. A virus that is outside of a host cell is known as a virion.
Viruses can infect only certain species of hosts and only certain cells within that host. Taxonomy and replication strategies of different types of RNA viruses. Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold influenza SARS MERS Covid-19 Dengue Virus hepatitis C hepatitis E West.
4 Which type of viruses can be directly used for translationA dsRNAB negative ssRNAC positive ssRNAD retroviruses positive ssRNA 5 If the hypothesis stating viruses evolved prior to living organisms on Earth is true the first type of viruses in the world were likelyA bacteriophageB DNA virusesC retrovirusesD RNA viruses. Genetic variation in prokaryotes. Some RNA viruses have their genome used directly as if it were mRNA.
Viruses are noncellular meaning they are biological entities that do not have a cellular structureThey therefore lack most of the components of cells such as organelles ribosomes and the plasma membrane. Impact of mutations on translation into amino acids. However if a virus contains a ssRNA genome the host ribosomes cannot translate it until the ssRNA is replicated into ssRNA by viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RdRP see Figure 611.
How is Translation Different from Transcription. Viruses are tiny infectious agents that rely on living cells to multiply. Klausner MD MPH Professor of Medicine and Public Health at UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine and Fielding School of Public Health.
SsDNAThe flow of information for ssDNA vClass VII. How transmission happens. Neither process can occur without the other.
The overview of the process of translation. They may use an animal plant or bacteria host to survive and reproduce. As such there is some debate as to whether or not viruses should be considered living organisms.
DNA viruses usually use host-cell proteins and enzymes to replicate the viral DNA and to transcribe viral mRNA which is then used to direct viral protein synthesis. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA but it may be double-stranded dsRNA. Their genomes are translated shortly after penetration into the host cell to produce the RdRp and other viral proteins required for synthesis of additional viral RNAs.
Translation takes place on ribosomes in the cell cytoplasm where mRNA is read and translated into the string of amino acid chains that make up the synthesized. A virion consists of a nucleic acid core an outer protein coating or capsid and sometimes an outer envelope made of protein and phospholipid. This is the currently selected item.
Protein translation tool at ExPASy - a tool which allows the translation of a nucleotide DNARNA sequence to a protein sequence. Retroviruses use DNA intermediates to replicate. Ribosomes Transcription and Translation.
RNA viruses usually use the RNA core as a template for synthesis of viral genomic RNA and mRNA. Some DNA viruses can also enter the host cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis. RNA viruses usually use the RNA core as a template for synthesis of viral genomic RNA and mRNA.
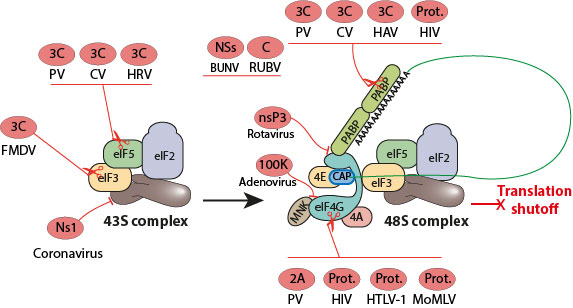
It has been reported that alphaviruses can use eIF2A instead of eIF2α in viral translation Ventoso et al 2006. Depending on the type of virus it can be spread through sneezes coughs sexual contact shared needles or fecal-to-oral transmission according to Jeffrey D. A virus must attach to a living cell be taken inside manufacture its proteins and copy its genome and find a way to escape the cell so that the virus can infect other cells.
Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of. If CoV mRNAs have similar requirements then eIF2α phosphorylation may not or less profoundly affect the translation of CoV mRNAs. Mutation as a source of variation.
Positive or plus -strand RNA viruses have genomes that are functional mRNAs. Both transcription and translation are equally important in the process of genetic information flow within a cell from genes in DNA to proteins. Which type of viruses can be directly used for translation.
Cells that a virus may use to replicate are called permissive. After the viral genome has been uncoated transcription or translation of the viral genome is initiated. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur.
An RNA virus is a virus which has ribonucleic acid as its genetic material. The main events in each stage of translation. The genetic information stored in DNA is a living archive of instructions that cells use to accomplish the.
DsDNADNA viruses with a dsDNA genome. Viral genomic ssRNA acts like cellular mRNA. Some RNA viruses carry enzymes which allow their RNA genome to act as a template for the host cell to a form viral mRNA.
Alternatively CoV mRNAs and host mRNAs may use a slightly different repertoire of translation factors. It is this stage of viral replication. DNA viruses usually use host-cell proteins and enzymes to replicate the viral DNA and to transcribe viral mRNA which is then used to direct viral protein synthesis.

22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts
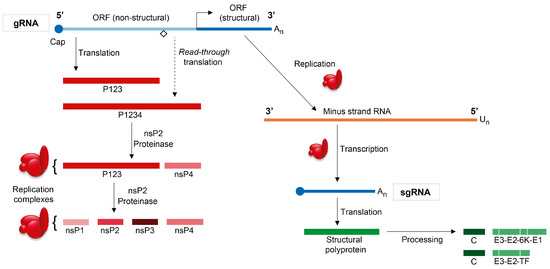
Viruses Free Full Text The Regulation Of Translation In Alphavirus Infected Cells Html
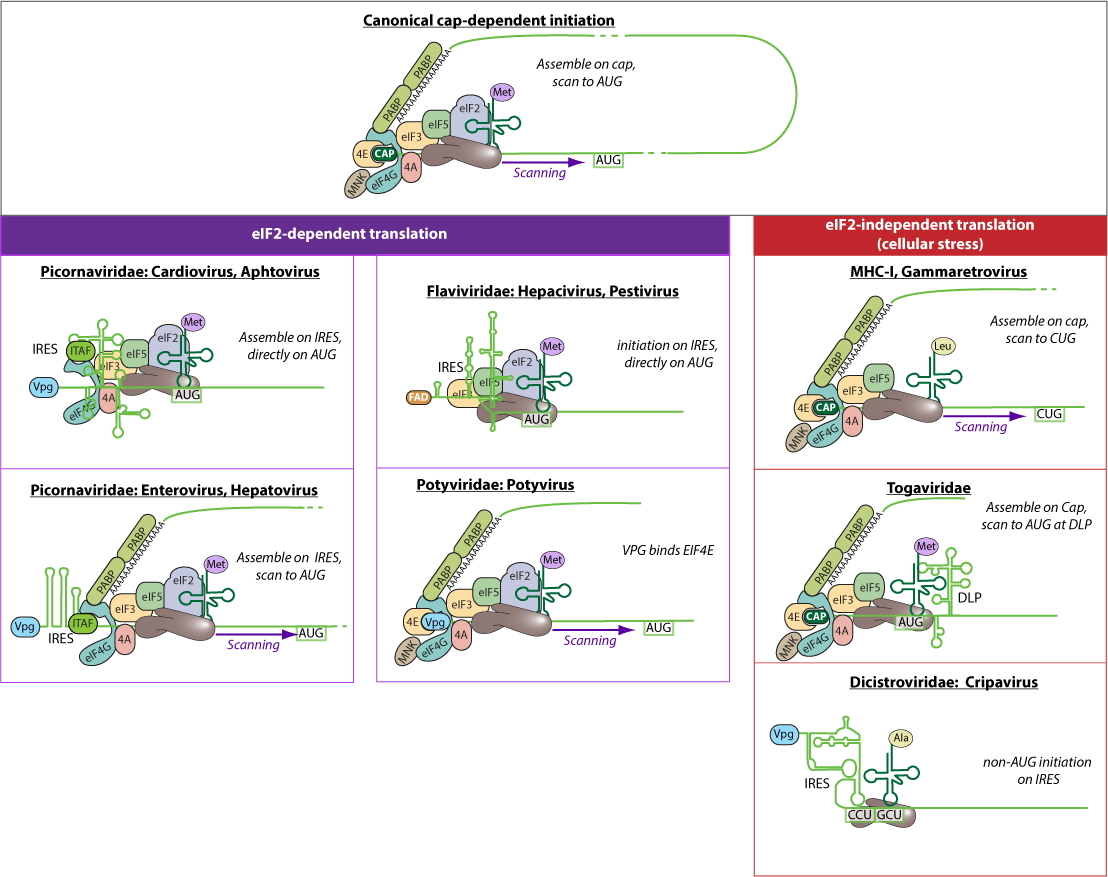

Comments
Post a Comment